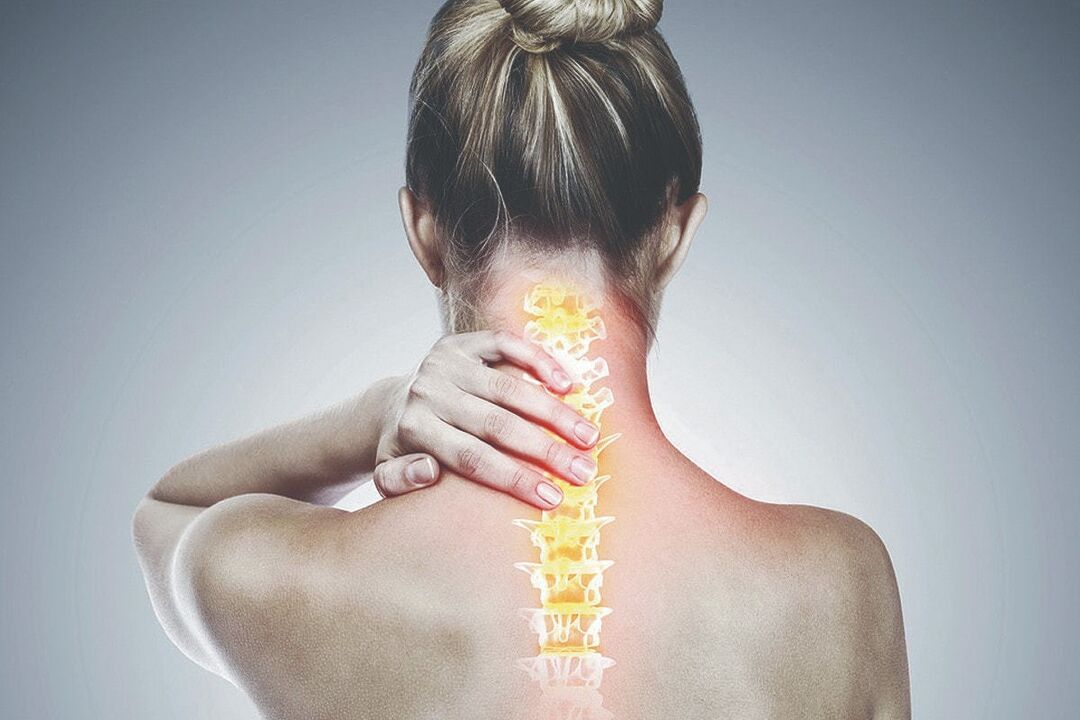
Cervical osteochondrosis -This is a degenerative-distorted lesion of the C1-C7 vertebrae and the intervertebral discs between them.Advanced pathology forms cause the compression of nerve roots of the spinal cord and the blood vessels that feed it, the development of paresis, paralysis, atrophy of muscle tissues and other dangerous conditions.That is why the detection of any symptom of osteochondrosis is the basis of a visit to a doctor who has the most relevant and complete information.He will talk about how cure cervical osteochondrosis and prevent the development of their complications.
How cervical osteochondrosis manifests
Find out how Cervical osteochondrosis manifests, impossible without a clear understanding of the mechanisms of the development of the pathological process.First must become familiar with the structural characteristics of the upper segment of the spinal column.Then, the cervical region is the most mobile part of the backbone responsible for neck movements, rotation and changes in the position of the head.It consists of seven vertebrae, two of which (Epistropheus and Atlant) have an atypical structure.In the intervals between these structural elements there are intervertebral discs, each of which is a core of the jacket, which is located inside the fibrous ring, from above and under the tissue of the cartilage covered with a layer.Its main functions are:
- ensure the mobility and flexibility of the column;
- Increasing the stability of the spine to the loads.
There are a number of factors that contribute to the destruction of the cartilage of the intervertebral discs of the cervical region.Osteochondrosis manifests itself based on factors such as:
- wounds;
- strong poisoning of the body;
- Excessive loads in the upper segment of the column (prolonged work on the computer, prolonged permanence in an unnatural pose, exhausting training, etc.);
- infections;
- Metabolic malfunction;
- inadequate nutrition, compliance with too strict diets;
- Small mobility;
- Congenital characteristics in the structure of the spinal column;
- hereditary predisposition to diseases of the musculoskeletal system;
- hypothermia;
- stress;
- elderly;
- alcohol abuse;
- smoking.
The degeneration of the cartilage under the influence of these factors leads to the deformation of the intervertebral disc.The core of the jacket changes to its edge, forming protrusion.With the thinning and advance of the connective tissue membrane (fibrous ring), a hernia is formed in the cervical region.The development of both pathologies is accompanied by intense pain, the displacement of the vertebrae, pressing the roots of the spinal cord and blood vessels.As a result, the victim has Cervical osteochondrosis.The progression of the disease is accompanied by:
- Degenerative-divophical change in the vertebral tissue;
- spinal deformation;
- the formation of osteophytes on the processes of vertebrates and motor segments;
- a decrease in the elasticity of ligaments;
- The loss of mobility in the cervical column.
The result of the development of pathology is the loss of work capacity and a significant decrease in the quality of life of a sick person.
How cervical osteochondrosis hurts: symptoms and signs
As Cervical osteochondrosis hurts It has differences compared to the symptoms of degenerative-dystophical processes that affect other spine segments.Since the vertebrae of the neck have a specific structure and are located very close to each other, any displacement of them causes acute pain due to a pinch of arteries or nerve fibers.
How does cervical osteochondrosis hurt, how to recognize and cure it?The main signs of pathology in the cervical region are:
- Pain in the neck area, shoulders, shoulder blades, chest, temples or neck, intensifying with head turns;
- a feeling of weakness in the hands due to the pinch of nerve roots;
- The occurrence of difficulties to turn the head in the direction associated with a violation of the natural structure of the intervertebral discs, as well as the formation of osteophytes, the appearance of a characteristic crystal in the neck;
- decrease in the sensitivity of the upper extremities;
- The general weakness and the appearance of dizziness, which causes blood vessels that supply useful nutrients to the brain.
- A decrease in visual acuity and auditory deterioration associated with circulatory disorders in cerebellum.
In Cervical osteochondrosis progression Several sequential stages pass with their clinical signs:
- There is a destruction of the cartilage.During this period, the symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis express themselves so weakly that patients do not notice or explain with stress and fatigue.
- The intervertebral disc is squeezed, cracks are formed on the surface of the fibrous ring.The disease is manifested by the general weakness, the pain in the neck and a slight numbness of the face.
- Intervertebral hernias are formed, blood vessels, nerve fibers are compressed.Patients complain about the appearance of pain in the occipital zone and dizziness.
- Bone tissues of damaged vertebrae grow, forming osteophytes.Patients have a sense of stiffness in movements.
In the last stages of the progression of cervical osteochondrosis, the clinical image is complemented with paralysis, paresis and muscles atrophy.In addition, the disease can be complicated by ischemia or stroke.
How to treat cervical osteochondrosis?
As Treat cervical osteochondrosis The doctor decides based on the exam results.The therapy program generally includes:
- Immobilization of the affected vertebral segment using a chantz necklace;
- Relief of the inflammatory process and pain when taking non -steroidal anti -inflammatory medications;
- weakening of muscle tension and the elimination of spasms using muscle relaxants;
- Elimination of pain with local drugs with irritating and anesthetic properties;
- Replacement of useful nutrient reserves in the body by taking mineral vitamins;
- Relief of a pronounced pain syndrome when establishing a novocaine block or intramuscular corticosteroid injections;
- Performing exercises that contribute to the decompression of nerve fibers and blood vessels, a decrease in neck load, normalize blood circulation in the affected segment and strengthen the muscles;
- Acupuncture, which allows to eliminate pain, accelerate the processes of tissue regeneration, relieve cramps, improve the general good of the patient;
- Try sports, contributing to the elimination of excess pressure on the cervical region (for example, swimming);
- Restoration of normal neck mobility by performing a manual therapy course;
- Activation of blood circulation, elimination of excessive tension in the muscles and elimination of pain with massage;
- Blocking inflammatory processes and the weakening of pain syndrome by performing a course of physiotherapeutic procedures (electrophoresis, magneto and laser therapy, narrowing, etc.).
With the intensive squeeze of the blood vessels and nerve roots in the neck, it is inappropriate to treat cervical osteochondrosis, as described above.In such clinical cases, patients are surgical intervention.As a rule, they conduct:
- Micro -surgical elimination of the damaged intervertebral disc (microdisctomy);
- Installation of implants capable of replacing the destroyed structural components of the vertebral-motor segment;
- Puncture that eliminates part of the jet nucleus (nucleoplasty);
- manipulations centered on the stabilization of vertebrae in the cervical region;
- Laser regeneration of damaged fabrics of the intervertebral disc.
An important role in the question of how to deal with and Cure cervical osteochondrosis Play a healthy lifestyle, abandoning cigarettes and alcohol, avoiding hypothermia, a long stay in motionless poses, stress and injuries.Patients are recommended to eat properly, excluded from the daily diet of smoked meats, fatty meat, sweets, semi -ends, baking, too salty plates, grapes, coffee, mushrooms, strong tea and carbonated drinks.
The complete and correct treatment allows you to slow down the development of the disease, restore the mobility of the spine and avoid complications.


















